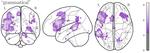
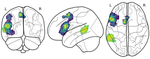
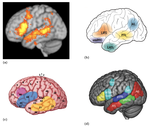
Language impairments, broadly known as aphasia are a common result of left hemisphere stroke. Aphasia looks different for every patient, but there are patterns across individuals between localization of damage and presentation of language symptoms. Two broad patterns of expressive syntactic deficits emerge: agrammatism and paragrammatism. Whereas agrammatism is characterized by omissions and reductions in syntactic structure (telegraphic speech), paragrammatism is characterized by substitutions and insertions, as well as breakdowns in hierarchical structure (sentence monsters).
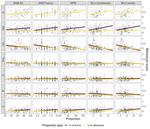
By closely analyzing transcripts of people with aphasia retelling the story of Cinderella, we can better characterize the nature of their expressive deficits, as well as understand how these deficits relate to focal brain damage.